
一种基于有机改性陶瓷材料制成的芯片,可以同时培养二维和三维细胞。
Introduction
思路:
过去十年中,三维细胞培养以其比二维细胞培养更多的保留了器官特异性功能,往往改善了体内外药物安全性和疗效评价的相关性,在药物筛选和验证中得到了越来越多的重视。
三维培养也存在大球体与厚基质样本的检测问题(增加的焦距、光散射),可能需要使用清除剂来提高深样本的分辨率,不可避免地增加了工作量。
大多数常用的微加工方法和材料都会产生垂直壁,对芯片上细胞球的形成和培养设置了一定的限制:
- 细胞最初彼此相距很远,在聚集过程中缺乏细胞间相互作用,导致孔与孔之间细胞球形成的重复率低和尺寸变化大。
- 增加初始细胞数或减少孔尺寸可提高重复率,但培养时间会变得有限。
U形微孔通常是细胞球培养的首选。然而,U形微孔的制造可能需要复杂的多步微加工流程。现有方法大多产生相对较浅的微孔,在延长的培养期内无法保留生长的细胞球。此外,大多数生物相容性聚合物缺乏各向同性的蚀刻工艺,与光刻技术生产的微器件相比,复制成型的微结构的后处理可能性(如金属化或空间选择性表面改性)往往是有限的。
本文中,作者描述了一种微加工方法,它有助于直接实现U形微孔,以便在微流控下生产小型三维细胞球。
- 由有机改性陶瓷材料(Ormocomp)制成,该材料在近紫外光范围内是光学透明的,并且具有内在的生物相容性,无需任何额外的涂层即可支持细胞粘附。
- 为了制造圆形(横截面轮廓)微孔,利用了Ormocomp的可控过度曝光,这有利于在单一光刻步骤中直接定制微孔的形状和深度。
- 利用等离子体处理的光刻(掩蔽)纳米功能化,通过原生Ormocomp的孔隙化和疏水涂层来定义局部细胞排斥表面(在微孔阵列中)。
因此,开发的概念有助于分别在天然和改性表面上的二维(单层)和三维(球体)中并排但孤立地培养细胞,有利于二维培养与三维培养并行使用。
The Concept of Parallel Culturing of Cell Monolayers (2D) and Cell Spheroids (3D) on Chip
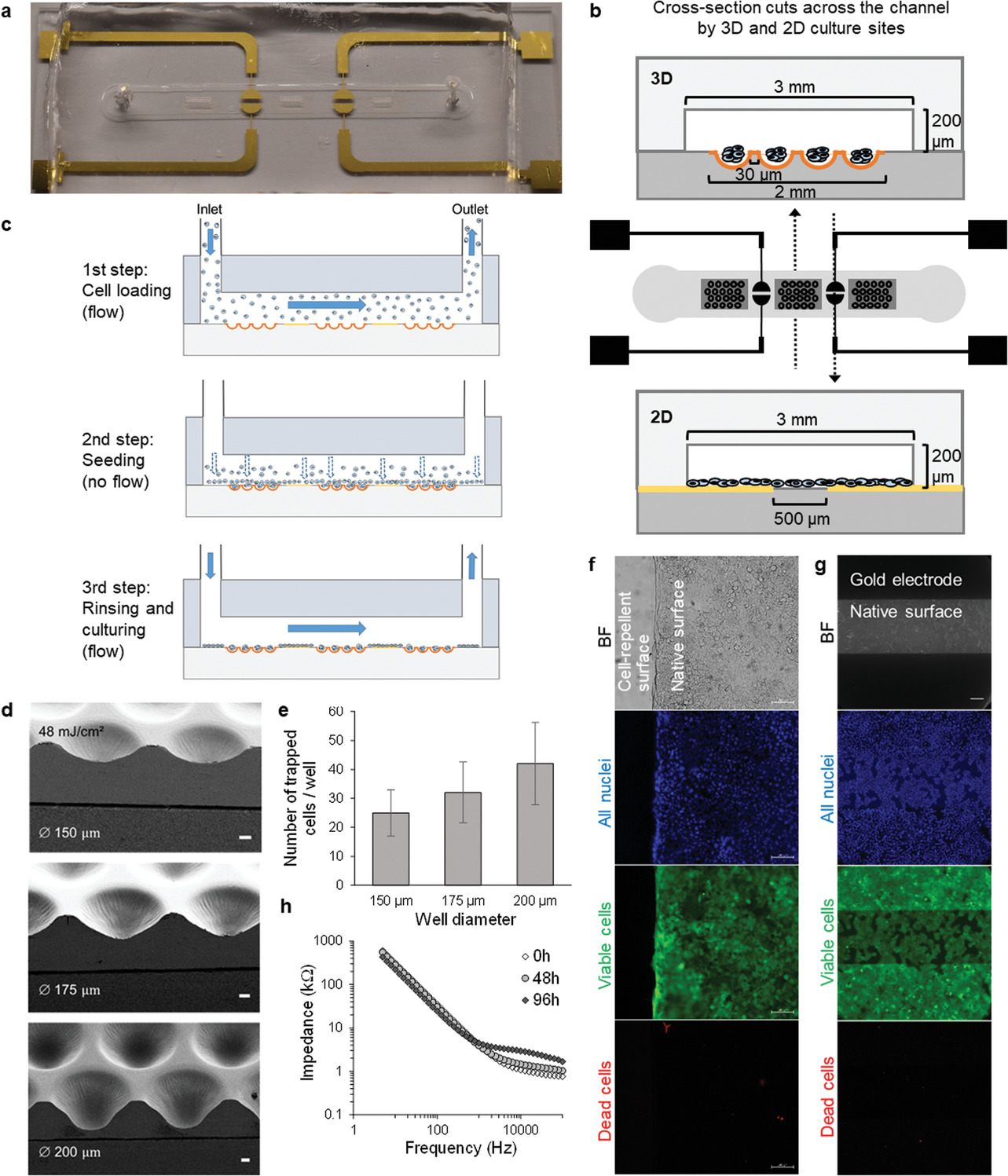
(a)实际芯片图。
(b)芯片示意图及二维/三维位点的横截面图。
(c)Ormocomp-PDMS芯片沿微通道的截面图以说明连续细胞接种步骤(前8 h为5.8 mm min-1,之后为2.3 mm min-1):
- 细胞加载;
- 在静态条件下30 min内接种细胞;
- 冲洗多余的细胞和二维/三维培养。
(d)恒定48 mJ cm-2紫外线剂量下,掩膜上微孔直径对所得微孔横截面轮廓的影响。
(e)微孔直径对捕获细胞数量的影响,成线性比例。
(f) 表面修饰对细胞粘附的影响,Ormocomp表面通过等离子体处理制成疏水和多孔状态,这被证明可以减少细胞粘附。
(g)在金电极上方培养的细胞(48 h)可以形成均匀的单层。
(h)在0-48-96 h记录的二维细胞培养的芯片阻抗谱表明,由于细胞增殖和细胞-细胞连接成熟,阻抗在16 kHz左右增加。
Validation of the Microfabrication Method
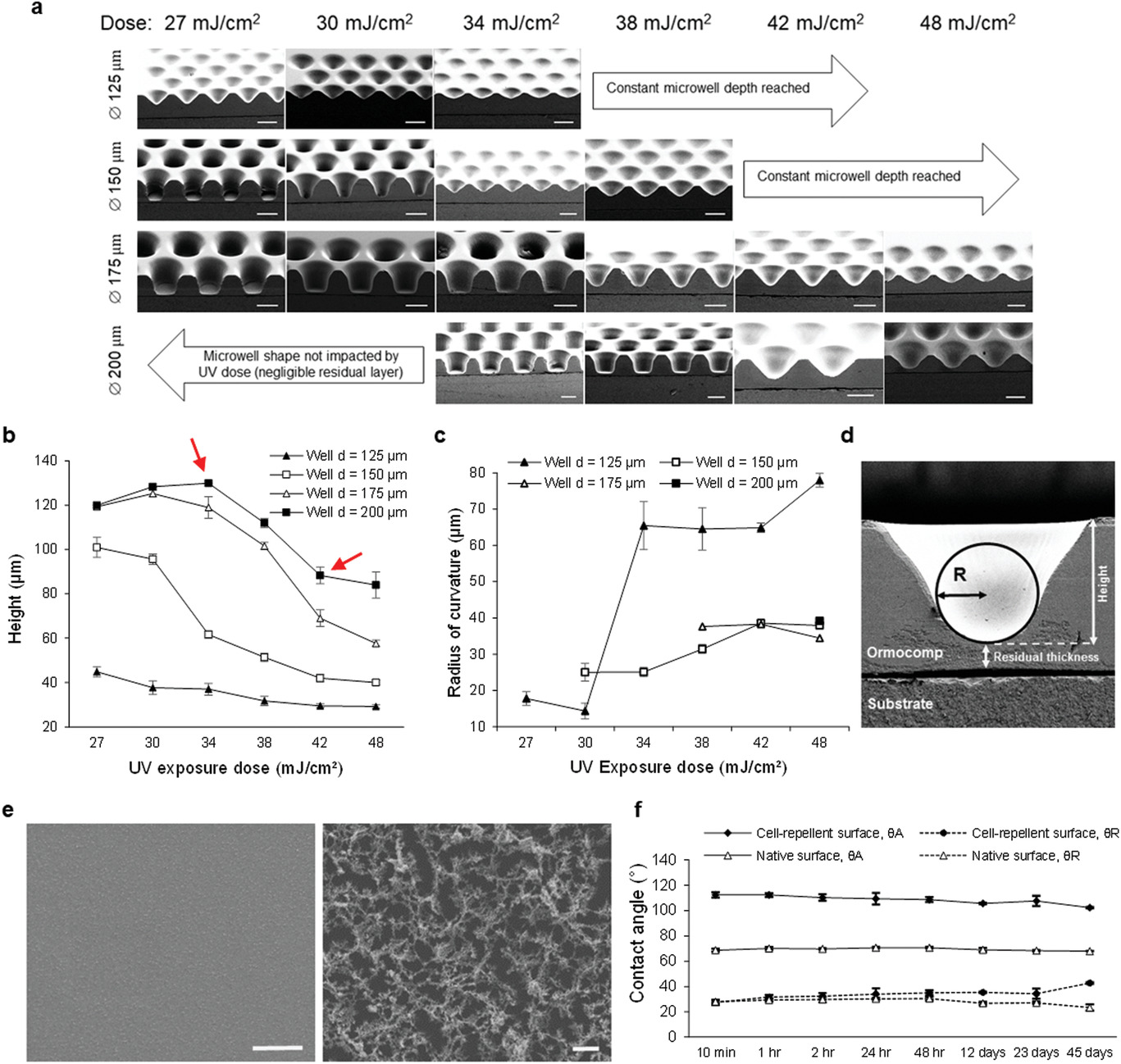
- (a)SEM图像中显示的微孔形状随紫外曝光剂量的演变,在达到与微孔直径相关的阈值剂量后,微孔底部残留层的厚度随UV剂量的函数线性增加,导致微孔深度线性减小直至饱和水平,即恒定的微孔深度。
- (b)由轮廓仪测量的微孔高度,箭头所指为200 μm孔的高度曲线的一段线性区域。
- (c-d)根据扫描电镜图像确定的曲率半径,如(d)所示。因此选定了48 mJ cm-2的暴露剂量用于所有后续实验,因为它为直径为150~200 µm的最大微孔尺寸提供圆形横截面轮廓。
- (e)等离子体孔隙化处理对Ormocomp表面的影响:无孔(左)和多孔(右)。
- (f)天然、细胞粘附性(亲水、无孔)和处理过的细胞排斥性(多孔化、含氟聚合物涂层)的Ormocomp表面的前进(θA)和后退(θR)接触角的稳定性作为时间的函数,与原始Ormocomp表面相比,表面润湿性发生了明显变化(疏水),即前进接触角增加并至少在一个月内保持稳定。但后退接触角不变,表明在改性表面上也留下了一些亲水部分。总之,这些特性导致在改性表面上有效的细胞排斥。
水接触角科普。
Characterization of the 3D Spheroid Formation on Chip

- (a)随着时间的推移(48-72-96 h),200 µm微孔中的细胞球生长。
- (b)细胞球在175和200 µm微孔中随时间线性增长。
- (c)细胞球体积和细胞核数量的相关性。
- (d)合并通道的三维构造图(F-肌动蛋白,绿色;和细胞核,红色)(顶部)、细胞核表面分析(中间)和整个细胞球体积的表面(底部)。较平滑的底面有助于细胞球生长到一定程度后(4 d)被释放,能后续用于流式细胞术、光片显微镜或光学投影断层扫描,
- (e)不同Z高度下,肌动蛋白和细胞核排布情况。
Method Validation for Drug Cytotoxicity Screening
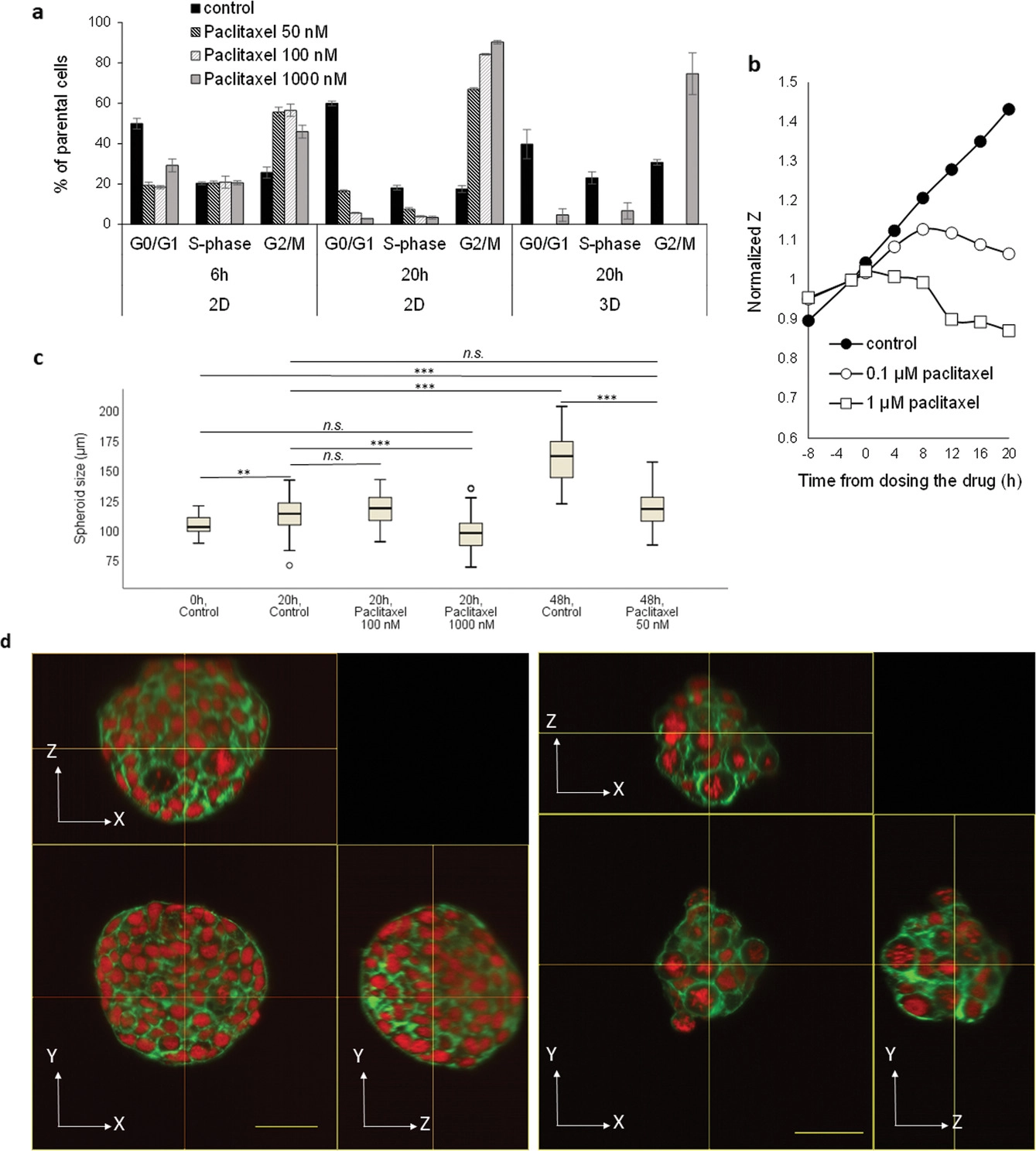
- (a)紫杉醇在标准96孔板上的二维细胞培养物中的肝癌Huh7细胞中,以及在芯片上培养的三维细胞球中,引起时间和剂量依赖性的细胞周期停滞(G2/M期)。
- (b)在16 kHz的芯片上阻抗传感器上观察到细胞单层完整性的破坏。可以看到高剂量的紫杉醇(1 μM)会导致细胞增殖立刻终止。
- (c)紫杉醇对细胞球大小的影响。在48 h(暴露后0 h)加入紫杉醇,并在暴露后20或48 h评估药物作用。
- (d)为了评估开发平台研究时间依赖性药物的影响,三维肿瘤暴露于50 nM紫杉醇(浓度远低于基于上述微流控二维/三维培养得到的急性细胞毒性阈值)。未暴露于紫杉醇(左)和暴露于高剂量(500 nM)紫杉醇 48 小时(右)的对照球体的正交投影,相应的总培养时间为96 h。细胞球被荧光标记为F-肌动蛋白(Actin-Green,绿色)和细胞核(DRAQ-5,红色)。与未暴露于紫杉醇的对照组相比,观察到细胞球大小、形状和细胞核形态的明显变化。
Conclusion
在这项研究中,作者利用一种有机改性陶瓷Ormocomp,建立了一个同时培养二维/三维细胞的微流控平台。主要:
- 在光刻步骤中创建圆形微结构;
- 基于等离子体处理的表面功能化,确保细胞排斥。
可以以可重复的方式培养小而均匀的细胞球,并在药物暴露后释放细胞球以进行进一步的芯片外分析。优势:
与原位荧光染色相比,能通过更先进的芯片外细胞表征技术和基于算法的图像分析进一步分析细胞球,从而使终点的选择多样化;
Ormocomp的固有表面特性支持细胞和金属的强粘附,这有助于在未修改的平面部件上实施二维细胞单层培养,并借助阻抗谱(通过集成电极)进行无创监测。
缺点在于通量较低,但能够在二维/三维培养中全面评估即时和时间依赖性药物对细胞事件的影响,可能会提供更全面和准确的体外预测。
Reference
Järvinen P, Bonabi A, Jokinen V, et al. Simultaneous Culturing of Cell Monolayers and Spheroids on a Single Microfluidic Device for Bridging the Gap between 2D and 3D Cell Assays in Drug Research[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(19): 2000479.



